Gratuitous ARP is either request or reply packet that is needed in some cases. usually when we assigned any ip on interface or host boot the first packet it send is GARP.
GARP packet have Sender and Target IP address same .Source mac address is of machine whereas destination mac is broadcast.
GARP IMP Question
1)GARP first packet is request or reply ?
2)GARP reply packet is unicast or broadcast ?
3)GARP opcode.
4)Why GARP is used ?
5) Messages or types of GARP packet ?
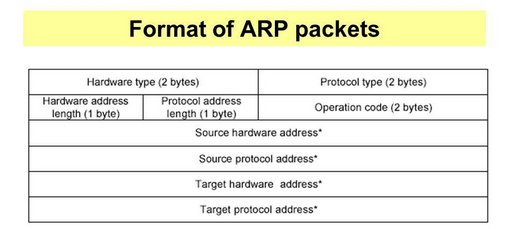
Learning acrimony—-Total 9 Field
HaPur HaPur SSOTT
In practical environment we only see GARP reply packet no GARP request is send.
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc5227#page-15
GARP have two opcode opcode 1 & 2. Remember opcode 1 is used for DAD(duplicate address detection) and opcode 2 is used for GARP.
There is two messages of GARP viz ARP probe (used for DAD) and ARP announcement (used to announce that machine own a particular ip address within the segment.
Consider one example where Switch has PC1 & PC2 and DHCP server connected.
Now PC1 is assigned with 192.168.174.111/24 ip address, PC2 is set to DHCP,
And DHCP server have only one ip i.e 192.168.174.111 left to assigned to PC2, and this ip is already configured on PC1 statically.
So what will DHCP assigned this ip address to PC2 or not.
Ans: DHCP won’t assigned this ip address to PC2 , because DHCP always do ARP probing to check if the ip which dhcp want to assigned is already assigned to any other host in the network or not. Since here 10.10.10.1 is already assigned to PC1 , then DHCP wont’t assigned this ip to PC2.
Now consider if 192.168.174.111 is not assigned to any host on the segment , in this case. DHCP will perform GARP probe message to check if there any duplicity of ip or if the ip that dhcp want to assigned it not used by any host. Let’s assume it is not used by any host, then DHCP will assigned 192.168.174.111 to PC2 and then once the PC2 have ip address assigned by DHCP, PC2 will send GARP announcement message to confirm other that PC2 own 192.168.174.111 ip. In return of GARP announcement it will get no reply which confirm only PC2 own this ip and no other host.