Today we will cover tcpdump tool. Tcpdump is a packet analyzer tool just like wireshark.
It run under command line interface. It help you to capture data packets on low level to understand what is going on inside the packet.
You can run tcpdump on linux/unix based operating systems.
Syntax for tcpdump
tcpdump <paramter>
e.g tcpdump -i eth0
Basic parameter of tcpdump
-i : Specify the network interface to listen on
-c : Number of packets which needs to be captured.
-w : Write the captured packets to a file for later analysis
-r : Read packets from a file instead of capturing from a network interface
-n: Do not resolve hostnames, display IP addresses only
-X: Display both hexadecimal and ASCII representations of packet data
-v: Increase verbosity level
-e: Print the link-level header on each dump line
-q: Quiet output, print less information
Operators in tcpdump:
– and ,&& —–This is used to concatenate two parameter
– or, || —–This is or operator used to match any one of the mentioned parameter
– not, ! —–This negate the mentioned parameter
– < – > —-Less than ,greater then parameter
Let’s take some example
Lets capture packets for eth0 interface for count of 4 packet in default mode.
I will now use any parameter
1. tcpdump -i eth0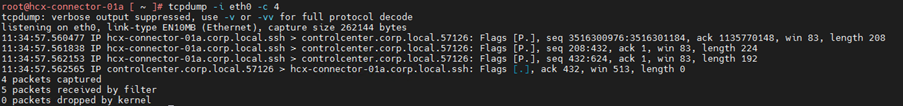
You can see we don’t have any header details here, lets add switch -e parameter to display link layer header.
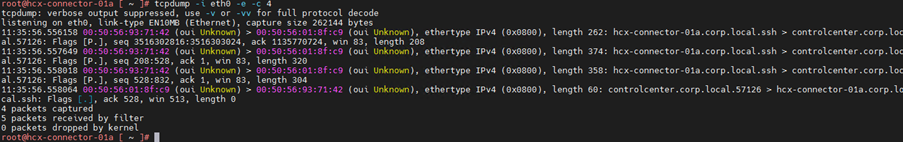
Now you can see the header details, mac address and ether type. Let’s add parameter -n this will show the host name as ip address in out packet capture.
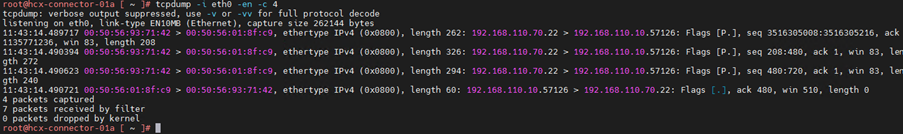
Now we see the source and destination as ip address instead of hostname. To get more details about the header we can add -v parameter
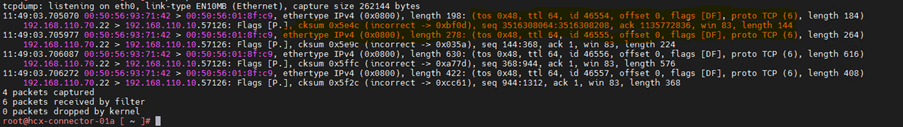
If you want to see more details about the header, then keep adding more verbose -v parameter.
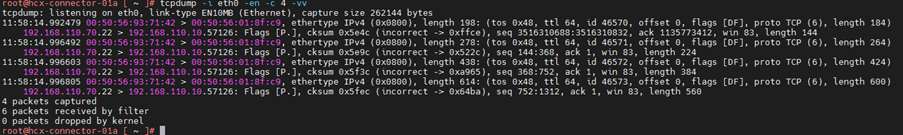
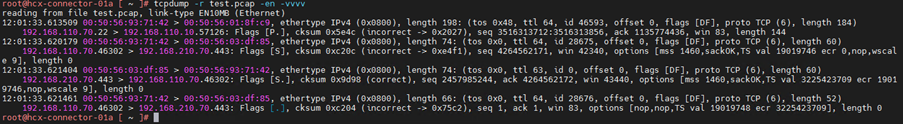
Now I want to write these packet details into file, so that I can read later or I can open in wireshark. Let’s use -w parameter to write file of tcpdump packet. I will save these files with name test.pcap


Read this file test.pcap by using -r parameter.

By default, read parameter do not show all packet header details. Use verbose parameter and other parameter to see details.
Few examples for different combination
1.Capture using mac address filter.
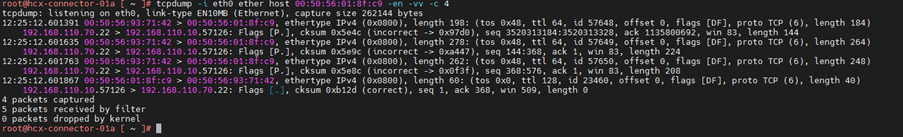
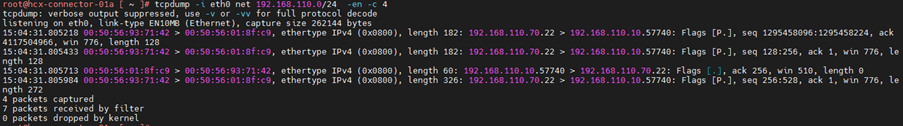
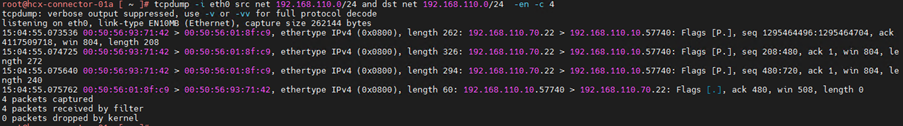
2.Capture all packet with ip address 192.168.110.70
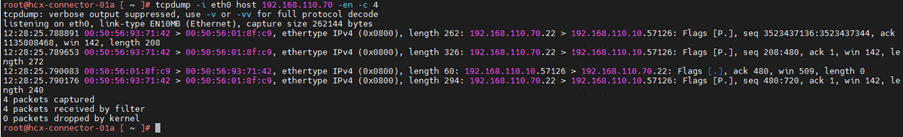
3.Capture packet with ip address 192.168.110.70 & 192.168.110.70. Here anyone can be source or destination.
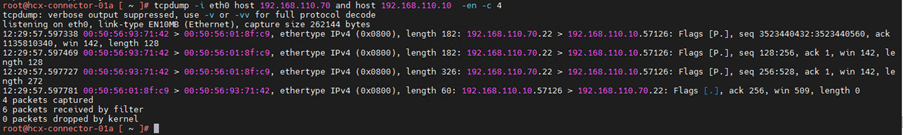
4.Capture packet with source ip address
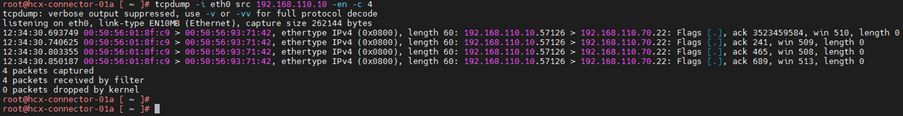
5.Capture packet with destination ip address
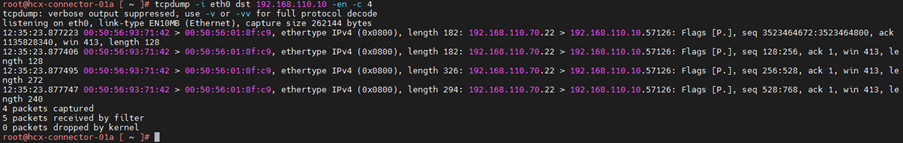
6.Capture packet of source and destination IP address
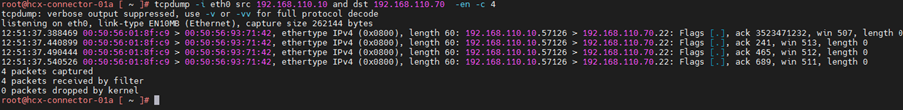
7.Capture packet by ports
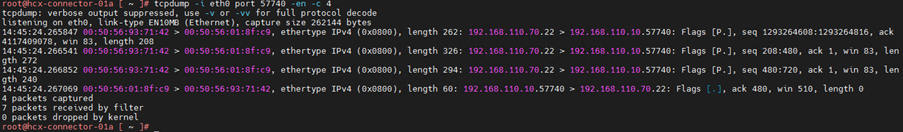
8.Capture packet on ip and ports
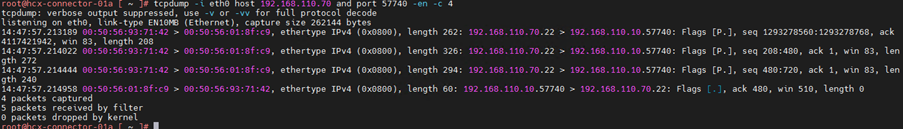
9.Capture using or operator or combination of or and operator
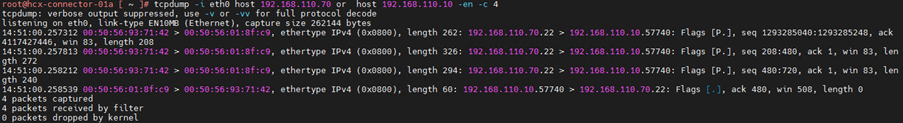
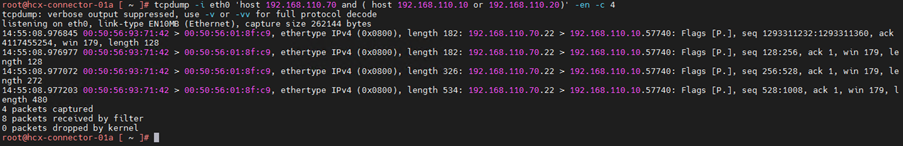
10.Capture using protocol address
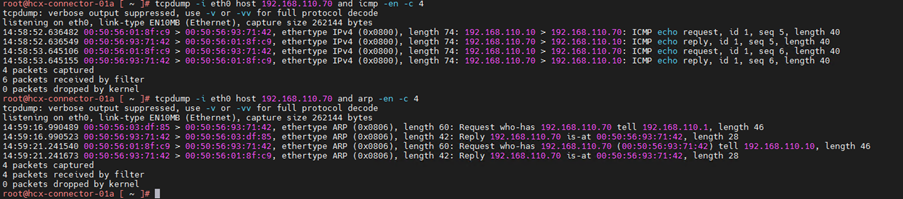
11.Using not operator to filter traffic
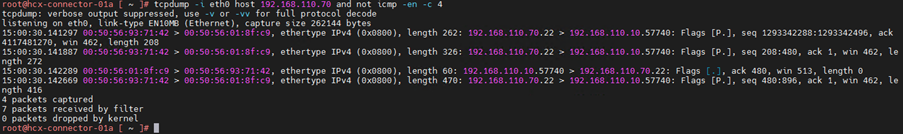
12.Capture the packets for range of ports
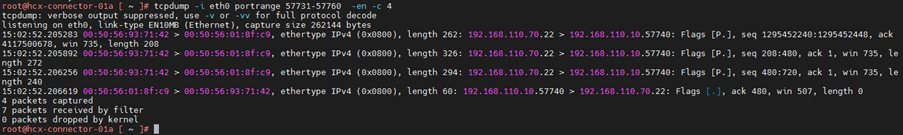
13.Capture packets of specific networks